UiPath Communications Mining
Monitor and automate business communications

From sending an email to responding to a customer request, every business conversation matters. But processing these communications has always been manual, costly, and inefficient. Until now.
UiPath Communications Mining turns every message into actionable data, in real time and on any communications channel.
Communications Mining combines AI and automation so you can automate your most common business requests and time-consuming conversations. From beginning to end.
$10M+
annual savings potential due to communications automation
20x
increase in customer recovery ROI potential
10%
of total email volumes automated end-to-end

Automate more across your business
Extend automation into entirely new business areas. Connect UiPath to all conversational channels—email, chat, calls, tickets, and more. Eliminate inefficient processes and automate transactional customer requests to cut costs and scale faster.

Deploy custom AI models in hours, not weeks
Our specialized large language model provides a strong foundation model on which businesses can build. Automatic labeling and annotation empowers any employee to rapidly train custom models the specifics of your business, with zero coding.

Enhance the customer experience
End the long wait times customers suffer when employees manually answer every communication. Communications Mining does more than streamline customer communications. Alerts will update you of any changes in service quality so you can get ahead of emerging issues.
White paper
The Ultimate Guide to Communications Mining
This white paper explores how businesses are leveraging AI to automate more, upscale their operations, and transform the service experience. All through the new technology category of communications mining.
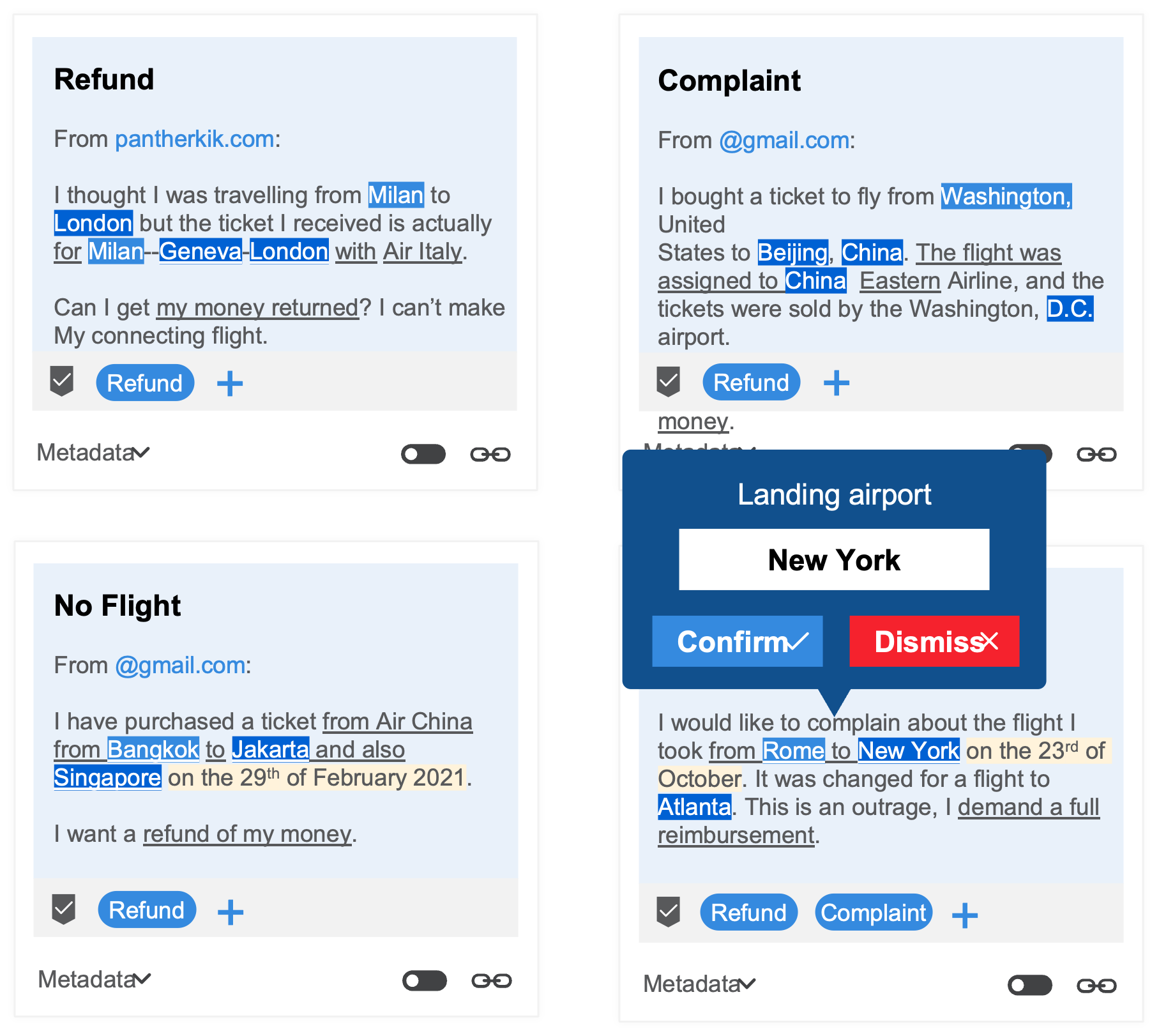
Communications discovery
Turn business conversations into actionable insights. Extract the most important data from any message–reasons for contact, data fields, and sentiment.
Communications discovery gives businesses insight into previously hidden processes and channels. This enables them to identify problems, inefficiencies, and new opportunities for elimination and automation.
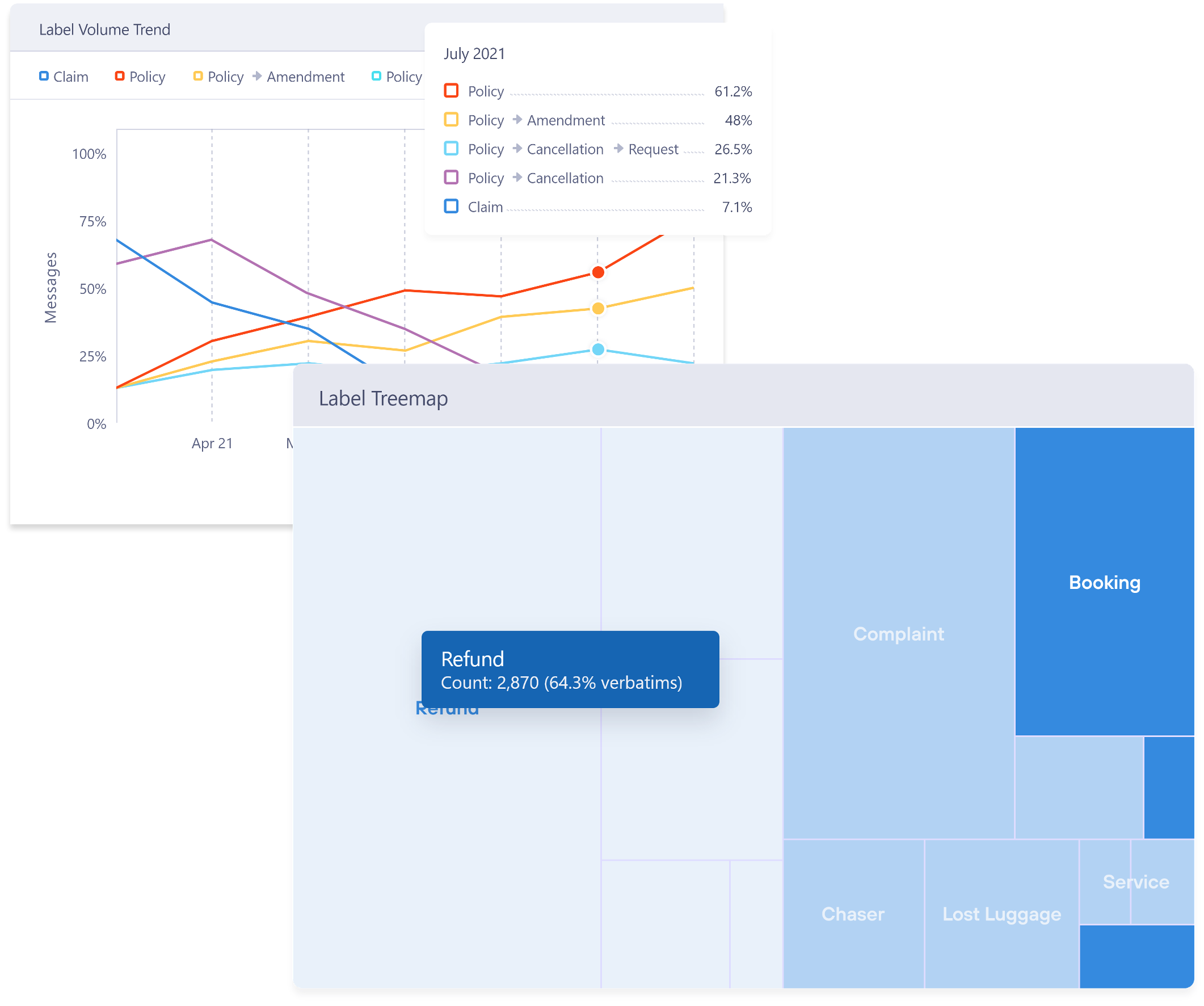
Communications monitoring
Gain a custom-filtered, real-time view of all service channels – extracting the information you care about most. Built-in analytics allows you to track trends, measure service quality and performance at all levels.
Custom, real-time alerts enable teams to respond to breaking issues in an agile way. Driving continuous improvement, being predictive instead of reactive.
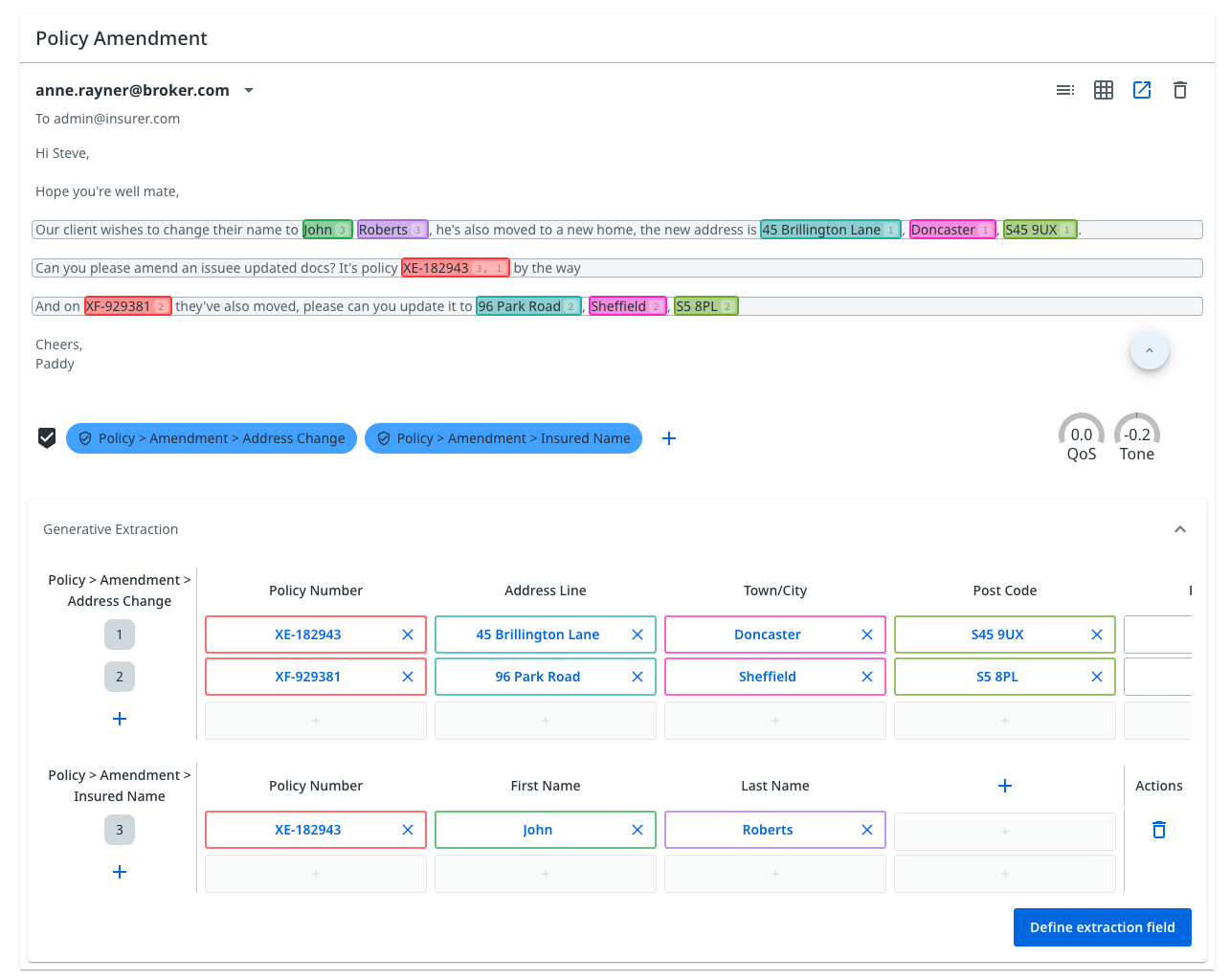
Communications automation
UiPath robots use the data created by Communications Mining to extend automation into service and conversation-based processes. This enables you to automate transactional requests and workflows.
Tasks like triaging emails, updating customer information, and case creation are now automated from end to end by UiPath.





1 / 5
Analyst Report
UiPath Communications Mining | ISG Provider Lens™
This analyst report explores the emerging enterprise category of communications mining, the acquisition of Re:infer by UiPath, and analyzes the business value of UiPath Communications Mining.
More to explore

Blog
Introducing UiPath Communications Mining

Blog
Communications Automation: Teaching Robots to Speak Our Language

Blog

